ACEA Biosciences officially joined the Agilent family September 1st, 2020. We are committed to providing flow cytometry and real-time live cell analysis solutions to support our customers.
For frequently asked questions about sales and support, read our FAQs
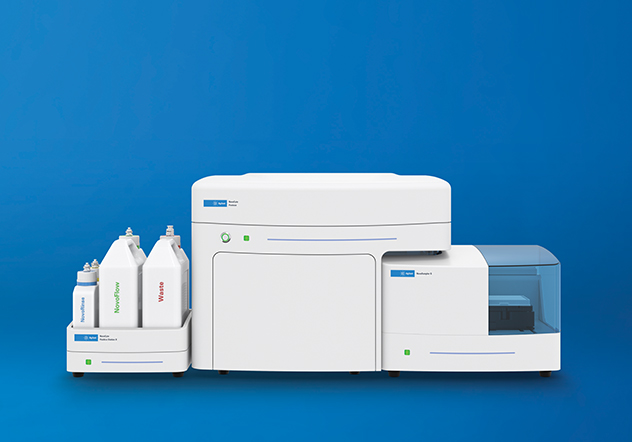

Agilent NovoCyte flow cytometers offer high quality data in an easy-to-use platform to save researchers time when acquiring and analyzing experimental data.
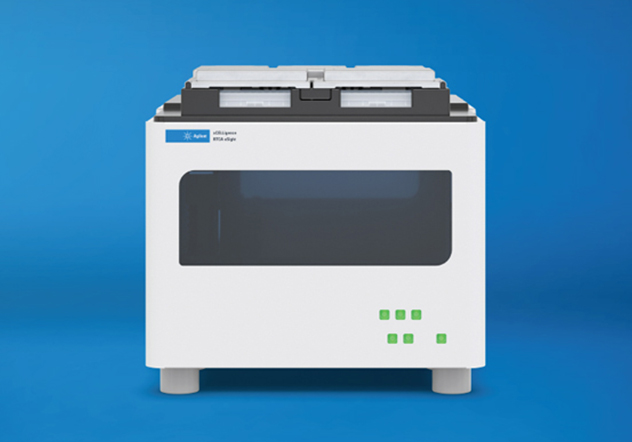

Agilent xCELLigence Real-Time Cell Analysis (RTCA) instruments use biosensors to continuously monitor cell behavior in a label-free manner.
Capture immune cell killing and measure functional potency in real time, without the use of labels.
Track virus-induced cytopathetic effects in real-time and greatly reduce workload and manual handling of samples.
Monitor cardiomyocyte contractility, viability, and field potential for use in disease modeling, safety toxicology, and drug discovery.
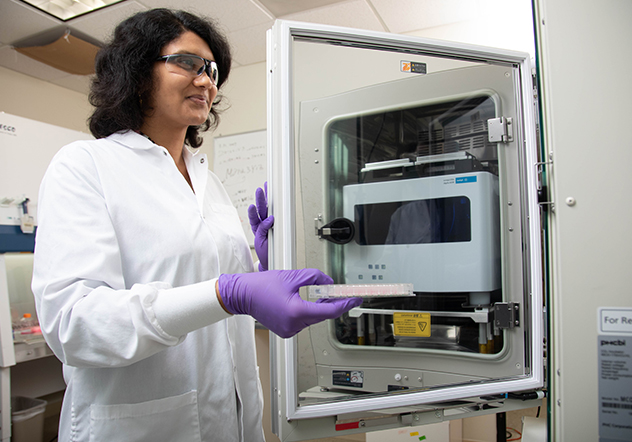

Capture the Most Critical Data Points
Are you spending your time running multiple assays, collecting timepoints and combining techniques to build a data set with confidence? In one instrument, capture sensitive changes in cell behavior by impedance monitoring and simultaneously visualize them by live cell imaging.
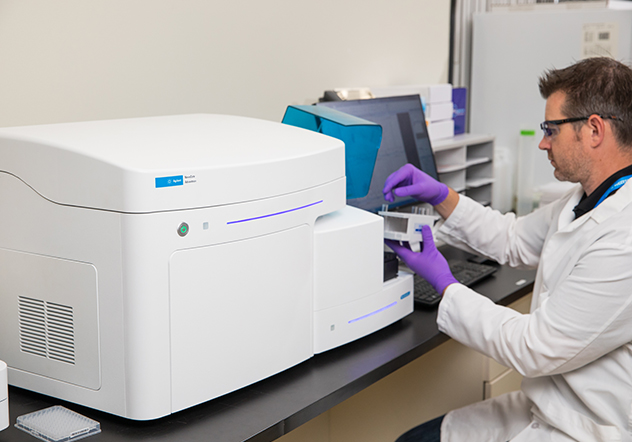

High Flexibility, High Throughput, High Quality
Discover an expanded set of capabilities that accomodates today's high-end and increasingly sophisticated multi-color flow cytometry assays. You now have the flexibility to choose from up to 30 fluorescence channels utilizing up to 5 lasers.
Flow cytometry experiments are now easier to perform with the NovoCyte's smart-design functionalities and intuitive NovoExpress software.
Fill out the form below and an Agilent representative will reach out to you.